Diamond Education
The 4 C'sExperienced
We offer a ‘Helping Hand’
At Skupham’s we understand it can be daunting when shopping for diamonds. Therefore, we have published this free resource for your perusal.
When setting a stone in a ring, our jeweller has experience working with “excellent,” “very good,” “good,” “fair” and “poor” diamond cuts. If you would prefer Skupham’s to source a quality diamond to complement our bespoke ring making service, we would be happy to offer a no obligation quotation and advice exploring the 4C’s.
Understanding
The 4 C’s of Diamonds
Every diamond, like a human fingerprint, has certain distinguishing characteristics. The 4C’s of colour, clarity, cut and carat weight are the globally accepted standards for assessing the quality of a diamond.
Purity
1. What is Clarity?
Diamond clarity is a measure of the purity and rarity of the stone, graded by the visibility of these characteristics under 10-power magnification. A stone is graded as flawless if, under 10-power magnification, no inclusions (internal flaws) and no blemishes (external imperfections) are visible.
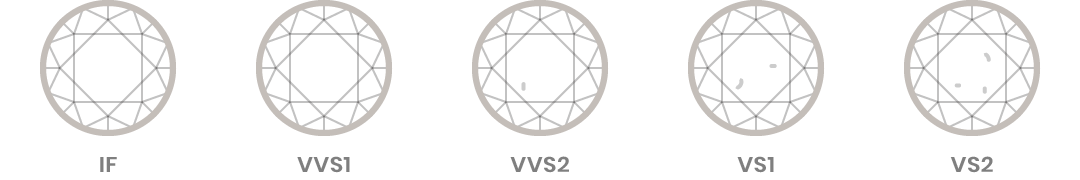
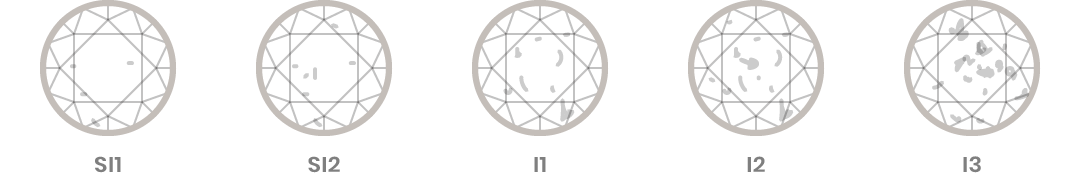
Diamond Clarity Descriptions
Diamond inclusions are internal flaws. Tiffany rejects any diamond with noticeable imperfections to the unaided eye.
FL – FL diamonds are Flawless
IF – IF diamonds are Internally Flawless
VVS1 VVS2 – VVS diamonds (1 and 2) are Very, Very Slightly Included
VS1 VS2 – VS diamonds (1 and 2) are Very Slightly Included
SI1 SI2 – SI diamonds (1 and 2) are Slightly Included
I1 I2 I3 – I diamonds (1, 2 and 3) are Imperfect
The gemmological standards in this section refer only to individually registered engagement diamonds set in certain ring styles.
Grading
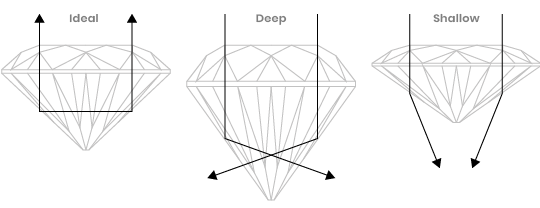
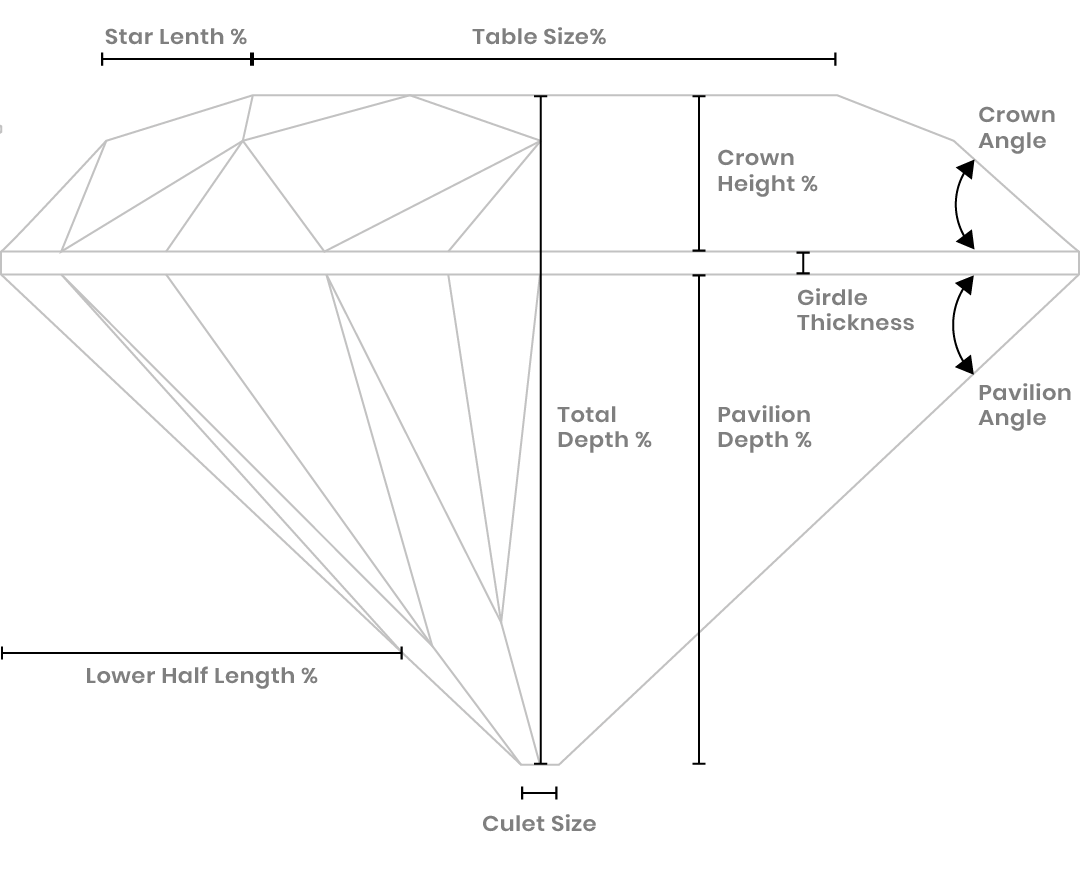
2. Why is Cut important?
Put simply, cut is responsible for the quality of a diamond’s sparkle. If a diamond is cut poorly, it will appear dull even if it has a high colour and clarity grade. If a diamond is cut well, it will reflect and refract light for maximum brightness and sparkle.
What Impacts Diamond Cut Quality?
Cut is the only one of the 4C’s that is affected by human hands. Two diamonds may have the same clarity, colour and carat weight, but cut is what determines whether one is superior to the other. Three factors alone determine a diamond’s cut:
Precision of cut
How the size and angles relate to the different parts of the stone.
Symmetry
How precisely the various facets of a diamond align and intersect.
Polish
The details and placement of the facet shapes as well as the outside finish of the diamond.
Natural
3. What is Diamond Colour?
Colour refers to the natural tint inherent in white diamonds. In nature, most white diamonds have a slight tint of yellow. The closer to being “colourless” a diamond is, the rarer it is. The industry standard for grading colour is to evaluate each stone against a master set and assign a letter grade from “D” (colourless) to “Z” (light yellow).
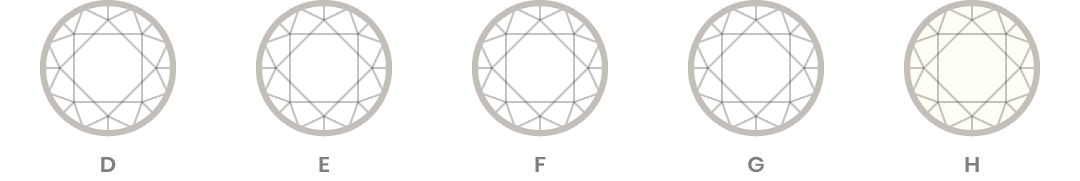
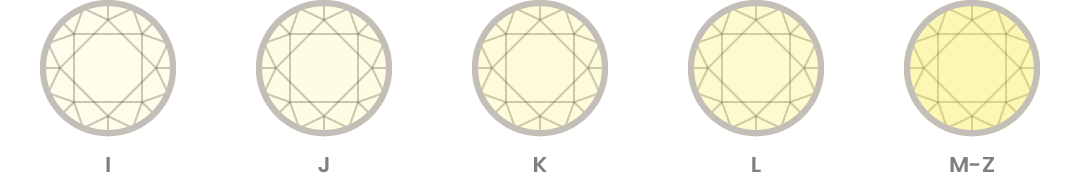
Does Colour Matter?
Colour is the second most important of the 4Cs because the colour grade directly affects the stone’s appearance. Diamonds with a poor colour grade can appear slightly yellow instead of the desired brilliant white. Additionally, some diamond sellers will not accept stones exhibiting strong or excessive fluorescence, which, in natural lighting, can give diamonds a milky appearance.
What's the Best Colour?
Among white diamonds, D colour diamonds are of the highest grade. D colour diamonds are in the “colourless” range on a diamond colour scale along with E colour diamonds and F colour diamonds. Fancy colour diamonds such as yellow or pink diamonds have their own colour grades.
Weight
4. What is Carat?
Carat denotes the weight of a diamond, not the size. Quality diamond manufacturers will measure diamonds to 1/1000th of a carat; one carat equals .20 grams.

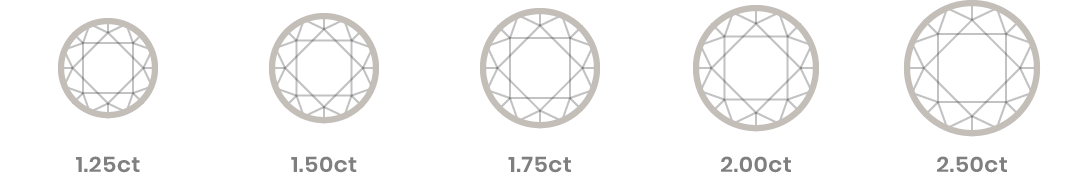
Diamond Sizing Descriptions
Carat weight can appear differently across different diamond shapes such as round brilliant, princess, pear, oval, cushion, marquise, emerald, radiant or heart. A diamond may have a higher carat weight without appearing larger and two diamonds of the same carat weight can vary in size if one is cut deeper than the other. In other words, it is important to note that carat weight does not necessarily denote size.
Sizes are shown for proportionality purposes. Images do not reflect actual carat size.

Skupham's Design
A Collaborative Process
1. Chat With an Expert
Designing a unique piece with Skupham's is a collaborative process. Together, you'll explore your design ideas, gemstones and precious metal options.
2. Design Approval
We then provides high quality sketches and provisional images of the piece that you want making, ready for you to approve or make any final amendments.
3. Create Your Ring
Once approved, our expert Jeweller gets to work in the Skuphams Workshop and will deliver your piece of Jewellery as designed, on time and to budget.